DATA ANALYTICS
How to determine and predict customer demand
Objective:
To obtain information about customer’s demand
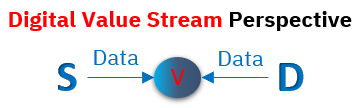
Taking the digital value stream perspective the main objective of data analytics is to determine customer demand and ultimately predicting it.
This requires the following steps:
- Obtain access to data about demand
- Digitisation of the data
- Analysis of the data
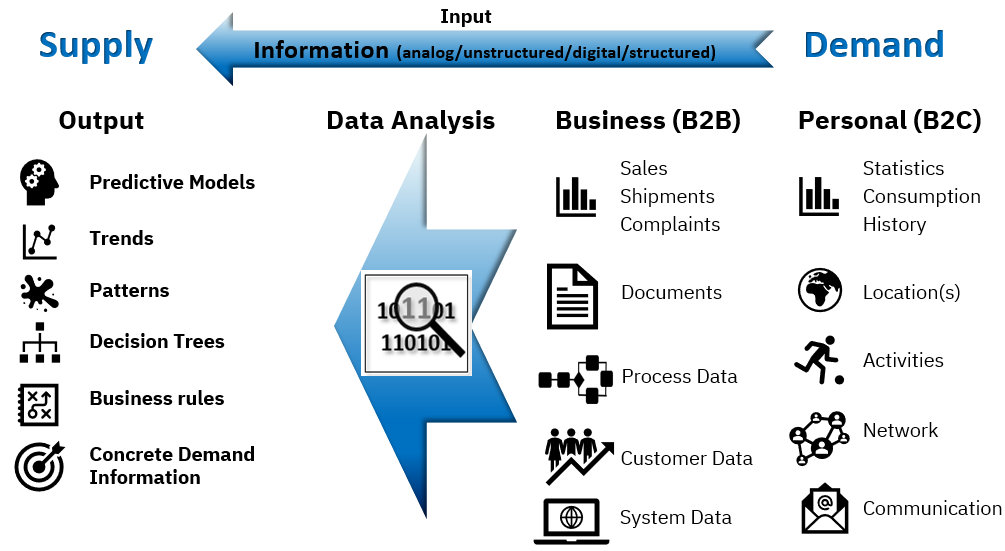
Examples of personal and business demand data and the output of the data analysis
Objective:
To identify business rules as a basis to automate processes
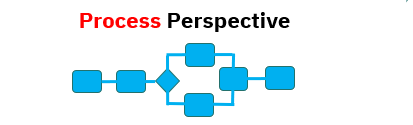
Taking the process-oriented perspective the value of data analysis is to automate the cognitive human activities along a processes. Human beings apply cognitive skills at various complexity levels to process data, i.e. categorising, analysing, synthesising and inferring decisions from such data. Prior to automation the human activities are defined through business rules (or descriptive models) reflecting the current level of business knowledge of how data has to be processed to create value internally or for the customer. The clarity and robustness of such business rules define the efficiency and effectiveness of the related processes and any automation efforts that build on business rules. For many companies clearly defined and robust business rules represent a challenge.
The following table compares the process-oriented and the digital value stream-based objectives and approach to data analytics.
COMPARISON
The following table compares the process-oriented and the digital value stream-based objectives and approach to data analytics.
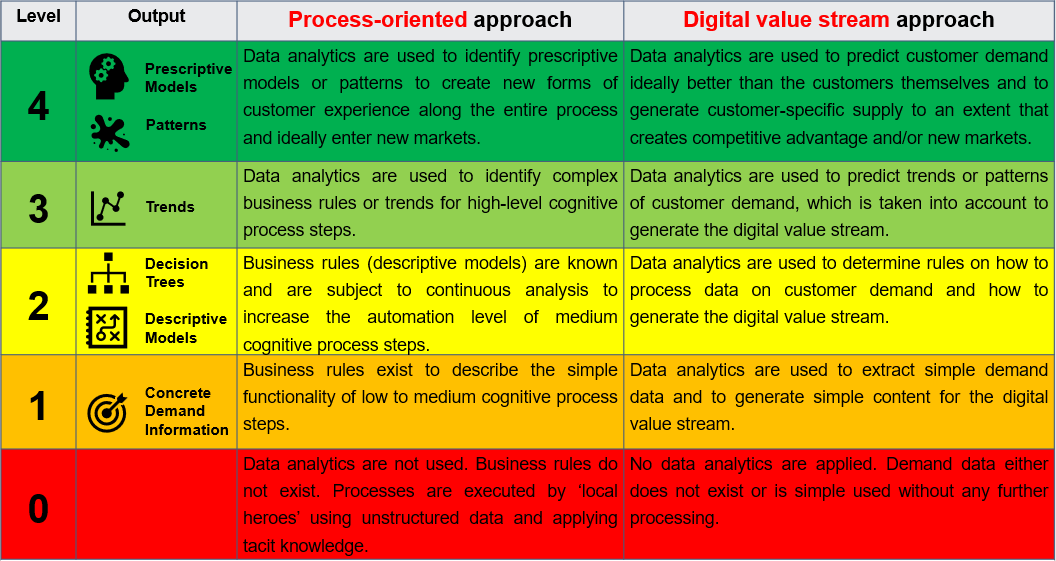
Level 3 and 4 reflect or build the basis for intelligent enterprise automation (IEA).
As such, data analytics is the starting point of IEA. Considering the enormous advance in data analytics companies are providing with a low-cost option to embark on IEA. The functionality of today’s state of the art data analytics tool is sufficient for most companies to reach level 3 or even 4. Assuming that they have structured data they can in short time evaluate the hidden value of their data and how to leverage it along their operation or customer-centric processes. Companies should not shy away from buzzwords such as big data or pattern recognition, but approach it experimentally in small steps and with little investment. The challenge is the access to demand data and creativity in applying technology to extract demand information.
Data analytics should have two drivers:
- Management asking questions related to current operations or user experience (for research to find out to what extent they can be answered).
- Data research exploring which insights can be extracted out of data
Both drivers should reinforce or stimulate each other like in a brainstorming meeting. It is difficult to give one driver more importance than the other. Innovation should come from both sides. Some companies have the origin of competitive digital advantage in data research others by innovative ideas from management on how to use data.
Questions to ask:
- What data is already available and to what extent is it structured?
- Digital value stream perspective: which data adds strategic value to improve our understanding of customer demand?
- Process-oriented perspective: which data add operational value to identify business rules as basis for process automation?
- How can I increase the strategic and operational value of available data?
- What other data would help to increase the strategic value and to what extent is it available?
- What unstructured data with potential operational or strategic value is available?
- How to transform unstructured in structured data?
Implementation steps:
- Inventorise the data that is available and categorise it in terms of potential operational and strategic value
- Link it to new forms of supply and think through how to create a (new) digital value stream based on this data.
- Link it to the processes that are using this data.
- Evaluate the impact of the new digital value streams on customers
- Evaluate the operational impact of cognitive process automation by determining the frequency and operating costs
- Test. Rethink. Modify.